In my new job role as a Test Engineer, knowing how to use Robot Framework for Automating Test Cases is crucial, to save time and to make testing more fun! As I’m going through this learning journey, I wanted to blog about it for anyone who is looking to start this journey and also to help me understand things in a better way.
There are plenty of good resources out there which explains the Robot Framework and it’s components. Best place to start would be the Robot Framework Documentation, which shows some interactive examples and very clear explaination. During my learning what I have come to realise is, there are lot of resources around Robot Framework used for Application Testing but there are not a lot of resources focused on Network Testing(or maybe I haven’t been thorough with my search!). That’s also one of the reaons for starting this blog, to give a Network Engineer’s perspective on Robot Framework and use the examples around networking to help us understand this better.
Software Version Check
For my first example, I wanted to create a Test Case to get the Junos Software Version from a device and compare it with an expected SW version.
- First component of our task would be to construct a Python code to get the SW version from a device. I’m using Juniper’s PyEz Library to get this done.
As you can see, it is a very simple script to gather facts and then from the output dictionary filtering out just the value of version using the key named version. If you have gone through the Robot Framework documentation, you would know that it is a Keyword driven framework. And in our case, we define the Keyword using a Python function. That’s why you are seeing a function check_version defined in the script which returns the Software Version.
from jnpr.junos import Device
def check_version(host):
dev = Device(host=host, user='robot', password='Junos12345')
dev.open()
return dev.facts['version']
- Second component would be constructing the Robot File (also called
Test Suite) with our Test Case.
*** Settings ***
Library pyez_version.py
*** Variables ***
${host} = 10.10.10.11
${expected_version} = 17.1R1.8
*** Test Cases ***
TestCase1
[Documentation] Checking if the SW version matches the requirement
${version_output} = Check Version ${host}
Should be equal ${version_output} ${expected_version} SW version doesn't match the requirement
Let’s look at some of the components of our Test Suite.
In the Settings section, we import the Library, which in our case is the Python script with the function defined to fetch the SW version.
*** Settings ***
Library pyez_version.py
Next, we have the Variables section, which as it says is where you’d define the Variables. There are multiple ways of defining Variables, we can do it as I have shown below or pass in a list, dictionary etc. host Variable here has the IP address of the device we need to connect, which would be sent as an input to the Python script. expected_version is the Variable used to enter the SW version we wish to test/match on the device.
*** Variables ***
${host} = 10.10.10.11
${expected_version} = 17.1R1.8
Now the Test Cases section. Documentation Keyword let’s us provide a description for our Test Case.
Then we see a version_output Variable, which stores the output returned by the Keyword Check Version. This Keyword is nothing but the function we defined in our Python script, just replace underscore with a space and if you look closely, it is case insensitive. After the Keyword, followed by a cell seperator(4 spaces), we provide the input Varibale for our function, which in this case is the IP address of the Host.
Next we see what is called a built-in Keyword, these come as a part of Robot Framework and doesn’t require any Library imports. Built-in Keyword here Should be equal compares two values and the Test Case is determined as PASS if they match and FAIL if they don’t. We mention the two values to be compared seperated by a cell seperator. And to customize a message in case of FAIL, we can define a message SW version doesn’t match the requirement, which would be displayed when the Test Case FAILs.
*** Test Cases ***
TestCase1
[Documentation] Checking if the SW version matches the requirement
${version_output} = Check Version ${host}
Should be equal ${version_output} ${expected_version} SW version doesn't match the requirement
With our required components in place, let’s execute the Test Case and see the results.
PS C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos> robot pyez_version.robot
==============================================================================
Pyez Version
==============================================================================
TestCase1 :: Checking if the SW version matches the requirement | PASS |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Pyez Version | PASS |
1 test, 1 passed, 0 failed
==============================================================================
Output: C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos\output.xml
Log: C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos\log.html
Report: C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos\report.html
PS C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos>
Our Test Case Passed! Now, let’s change the expected SW Version and see if Robot can detect it and fail our Test Case.
PS C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos>robot pyez_version.robot
==============================================================================
Pyez Version
==============================================================================
TestCase1 :: Checking if the SW version matches the requirement | FAIL |
SW version doesn't match the requirement: 17.1R1.8 != 16.1R1.8
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Pyez Version | FAIL |
1 test, 0 passed, 1 failed
==============================================================================
Output: C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos\output.xml
Log: C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos\log.html
Report: C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos\report.html
PS C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos>
Now our Test Case Failed! And we can clearly see that the expected SW version we passed, 16.1R1.8, did not match the extracted SW version, 17.1R1.8!
Robot also let’s us pass the Variable from the command line, i.e. instead of hardcoding the expected_version varibale in the Test Suite, we can input this from the command line. Let’s see how to do it, updated Test Suite looks like below, only change is that I have commeneted the expected_variable under the Variables section.
*** Settings ***
Library pyez_version.py
*** Variables ***
${host} = 10.10.10.11
#${expected_version} = 16.1R1.8
*** Test Cases ***
TestCase1
[Documentation] Checking if the SW version matches the requirement
${version_output} = Check Version ${host}
Should be equal ${version_output} ${expected_version} SW version doesn't match the requirement
To enter the Variable from command line, we use -v key, as shown below.
PS C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos>robot -v expected_version:16.1R1.8 pyez_version.robot
==============================================================================
Pyez Version
==============================================================================
TestCase1 :: Checking if the SW version matches the requirement | FAIL |
SW version doesn't match the requirement: 17.1R1.8 != 16.1R1.8
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Pyez Version | FAIL |
1 test, 0 passed, 1 failed
==============================================================================
Output: C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos\output.xml
Log: C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos\log.html
Report: C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos\report.html
PS C:\Users\User\PycharmProjects\Robotframework\Junos>
Another great feature Robot Framework offers is, Test reports and logs are generated in html which makes reading it very easy using a web browser. Path to the Log and Report is printed out to the Console as you can see in the above output.
Report for our Test Suite is shown below 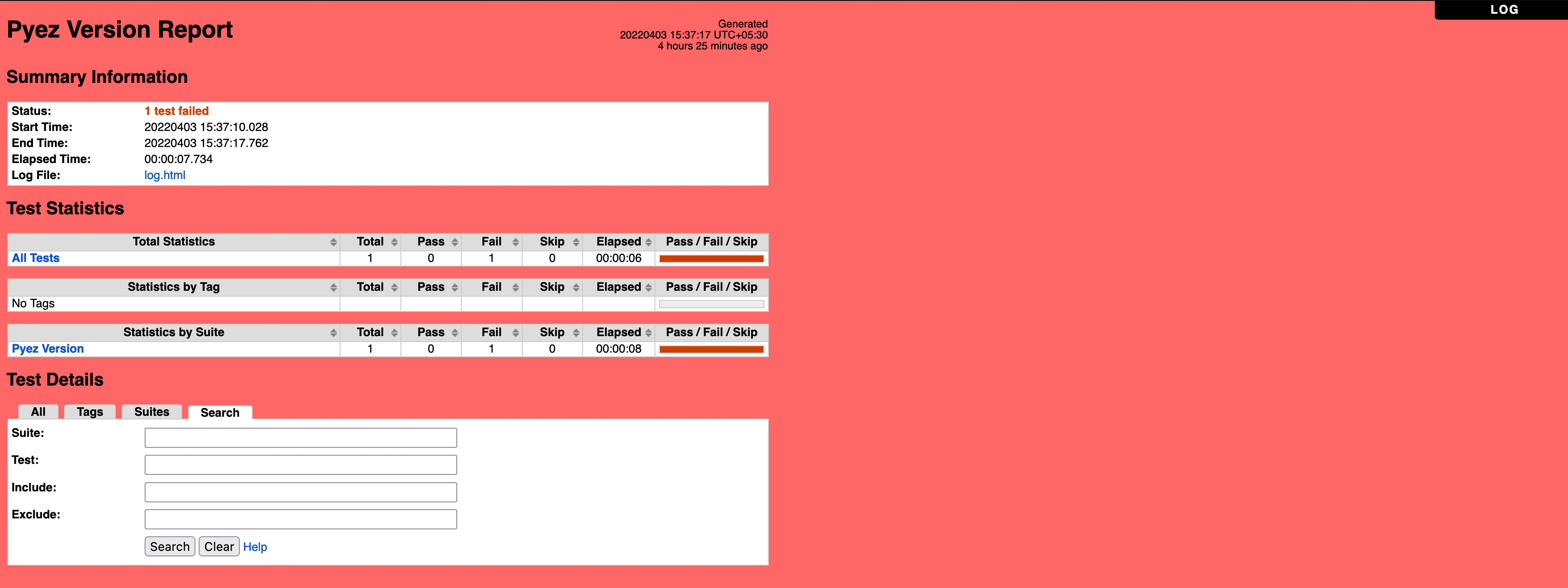
We can toggle to the Log file by clicking on LOG displayed on the top right corner, LOG file our Test Case is shown below 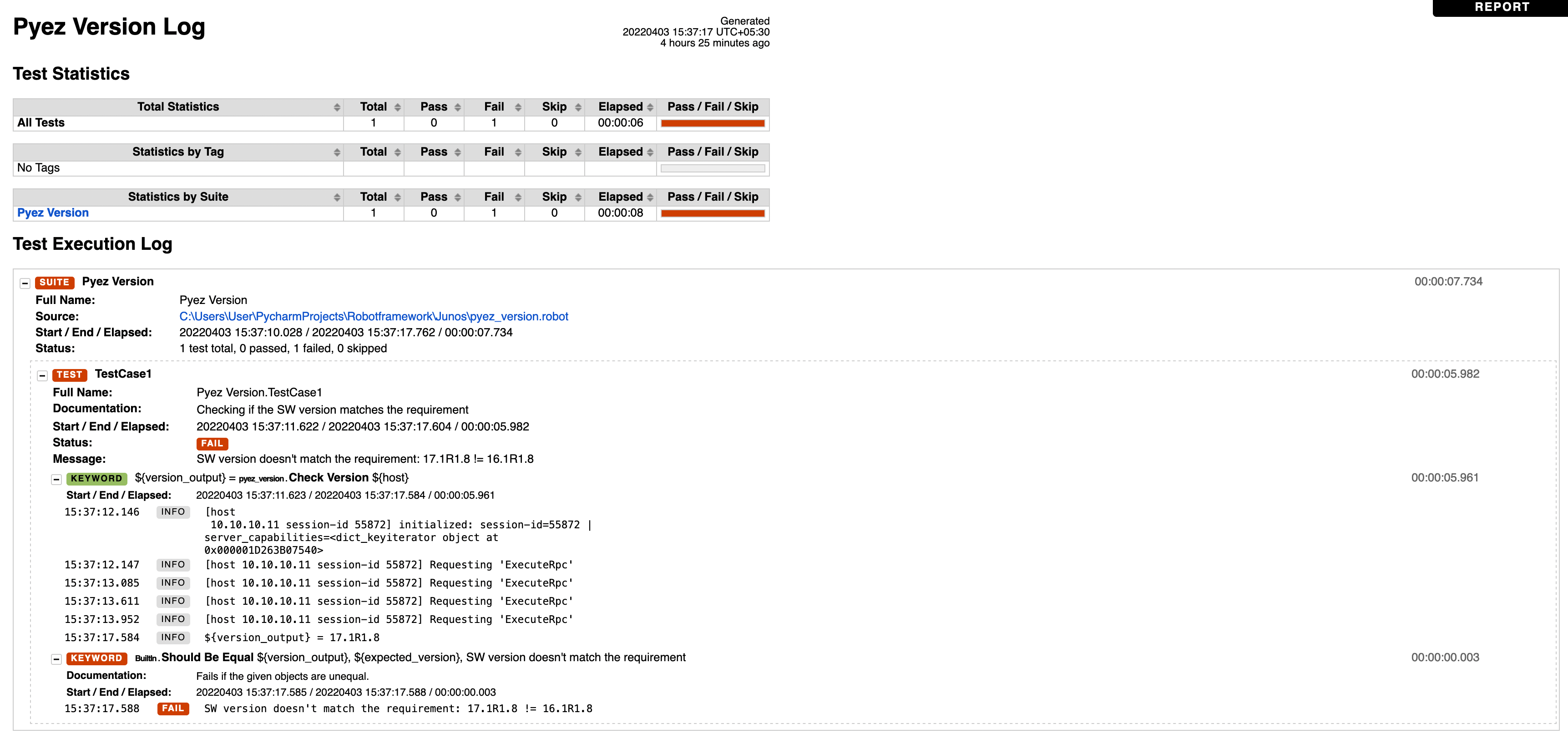
And with that we have completed our first Testing using Robot Framework! Hopefully, you and I can now explore more and start Testing complex network related things.
As this is my first take at blogging, I’d really appreciate your feedback so that I can keep getting better at this!
Dependencies
You need to have Robot Framework installed and any other dependencies based on your Python script. In this example, that would be PyEz.
python -m pip install robotframework junos-eznc